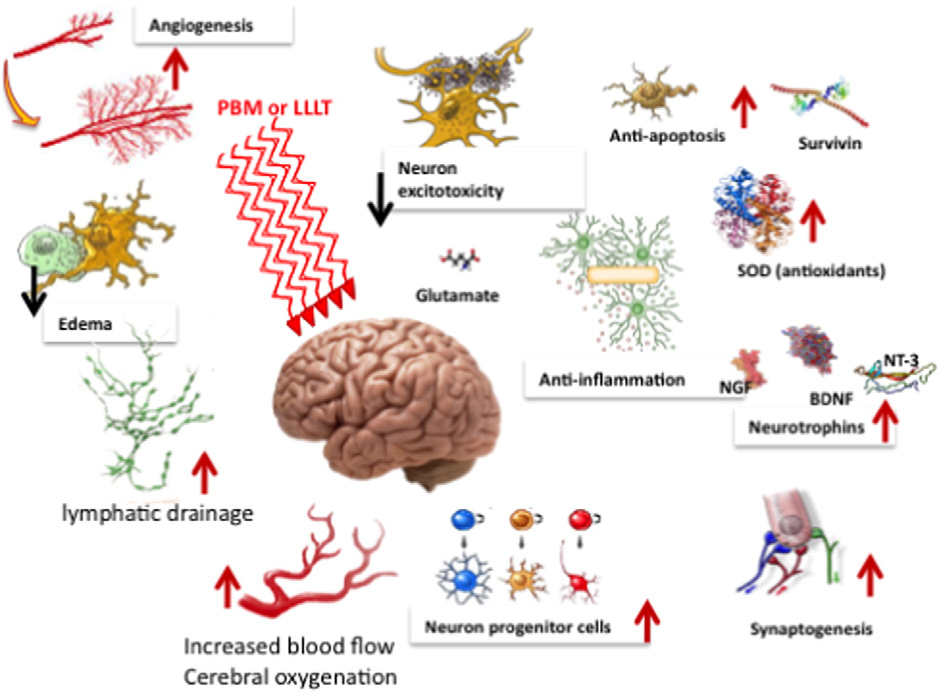
Cytochrome C oxidase (CCO, also known as complex IV) is a specific structure in mitochondria that ACTS as a photon receptor and thus plays the PBM effect.PBM prevents respiratory inhibition (and correspondingly reduces energy storage) in stress cells by isolating nitric oxide (NO) and reversing the shift of oxygen in cytochrome C oxidase.This triggers transcription factors that alter gene expression levels.The binding of nitric oxide (NO) to copper (or heme) centers in the mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase (CCO) inhibits cell respiration.But cytochrome C oxidase, which absorbs red or near-infrared (NIR) light, dissociates nitric oxide, restoring oxygen, increasing cellular respiration, and forming adenosine triphosphate (ATP).This triggers a cascade of intracellular reactions involving nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and cyclic adenosine phosphate (cAMP) that produce beneficial effects of PBM.